The Musical Note
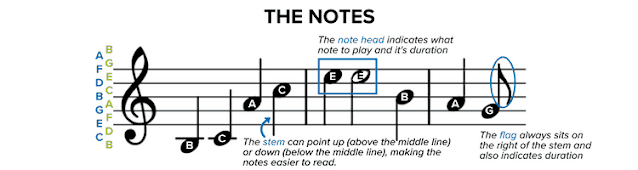
Notes on the staff tell us which note to play on our instrument and how long to play it. There are three parts of each note; is the note Head, the Stem, and the Flag.
Every note has a note head, either filled (black) or open (white). Where the note head sits on the staff (either on a line or space) determines which note you will play. Sometimes, note heads will sit above or below the five lines and four spaces of a staff. In that case, a line (known as a ledger line) is drawn through the note, above the note or below the note head, to indicate the note letter to play, as in the B and C notes above.
The note stem is a thin line that extends either up or down from the note head. The line extends from the right if pointing upward or from the left if pointing downward. The direction of the line doesn’t affect how you play the note but serves as a way to make the notes easier to read while allowing them to fit neatly on the staff. As a rule, any notes at or above the B line on the staff have downward pointing stems, those notes below the B line have upward pointing stems.
The note flag is a curvy mark to the right of the note stem. Its purpose is to tell you how long to hold a note. We’ll see below how a single flag shortens the note’s duration, while multiple flags can make it shorter still.
The note flag is a curvy mark to the right of the note stem. Its purpose is to tell you how long to hold a note. We’ll see below how a single flag shortens the note’s duration, while multiple flags can make it shorter still.


Comments
Post a Comment